SAP FICO Module – Complete Finance Module Overview
Learn SAP Financial Accounting (FI) with real-time access, expert guidance, and placement support at Think Tree.
Grade a+ Course
Content is Benchmarked by SAP
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
Level 3 – Expert Level Course
Course is designed to prepare you to become a SAP Consultant
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
What is SAP FICO Module – Complete Finance Module Overview
What is SAP Finance Module
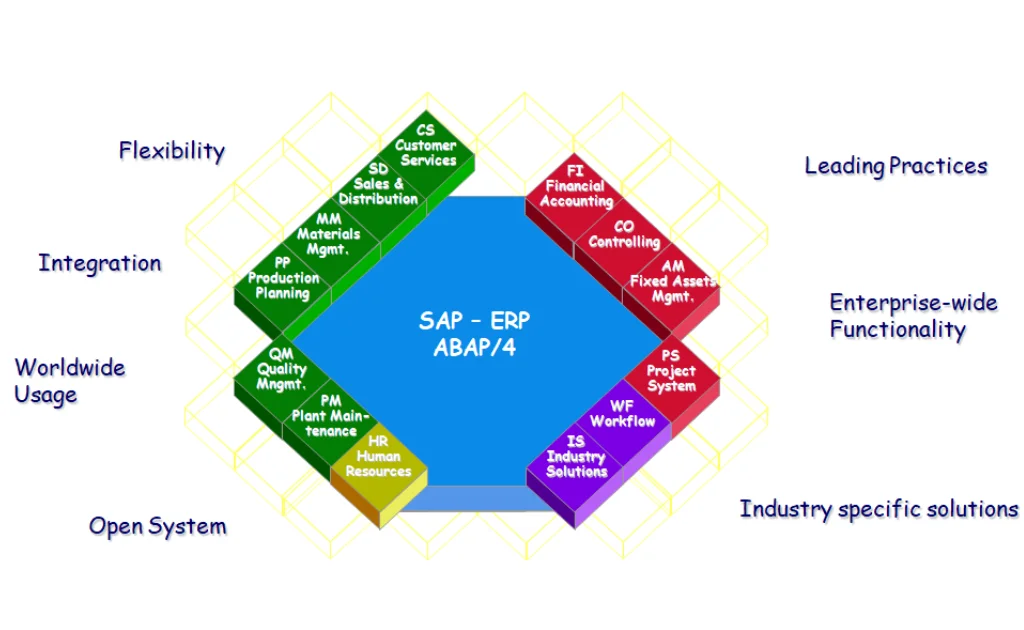
The Finance (FI) module in SAP is a core component of the SAP ERP system that helps businesses manage all their financial transactions, accounting data, and external reporting requirements in a centralized and reliable way.
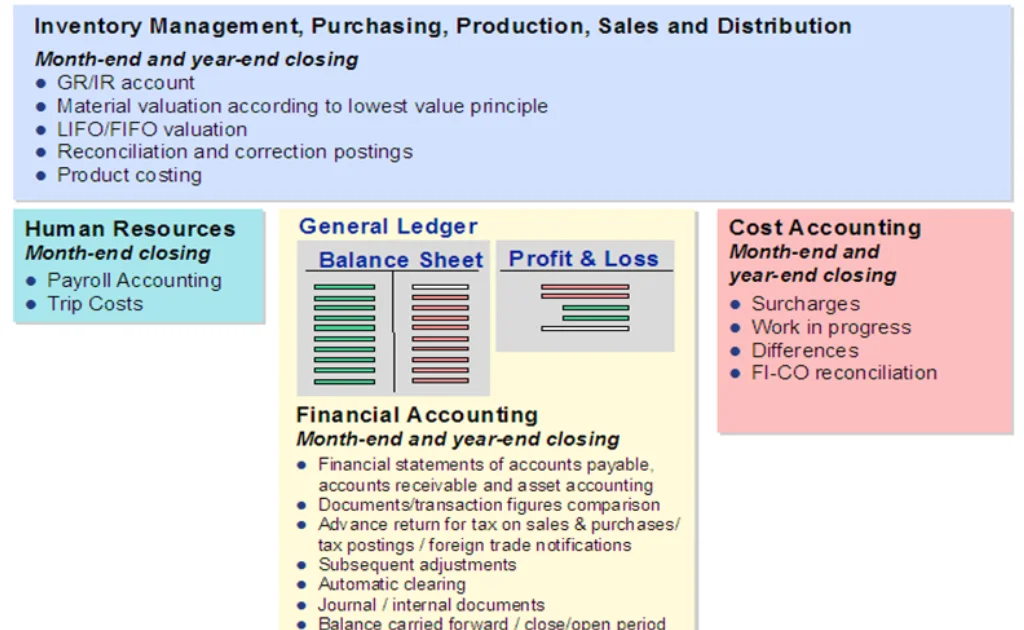
Key Functions of SAP FI:
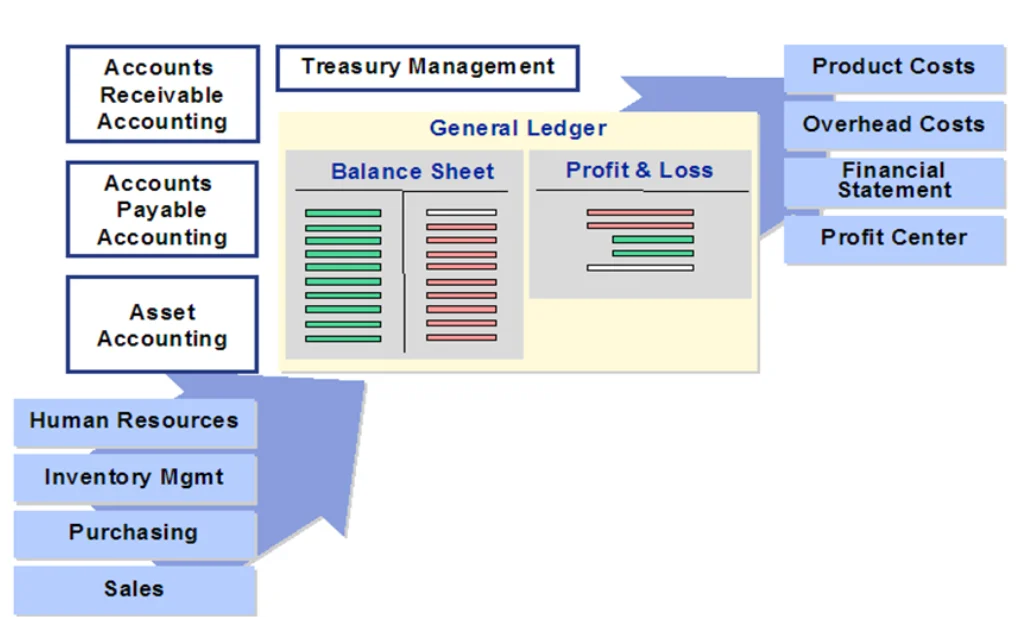
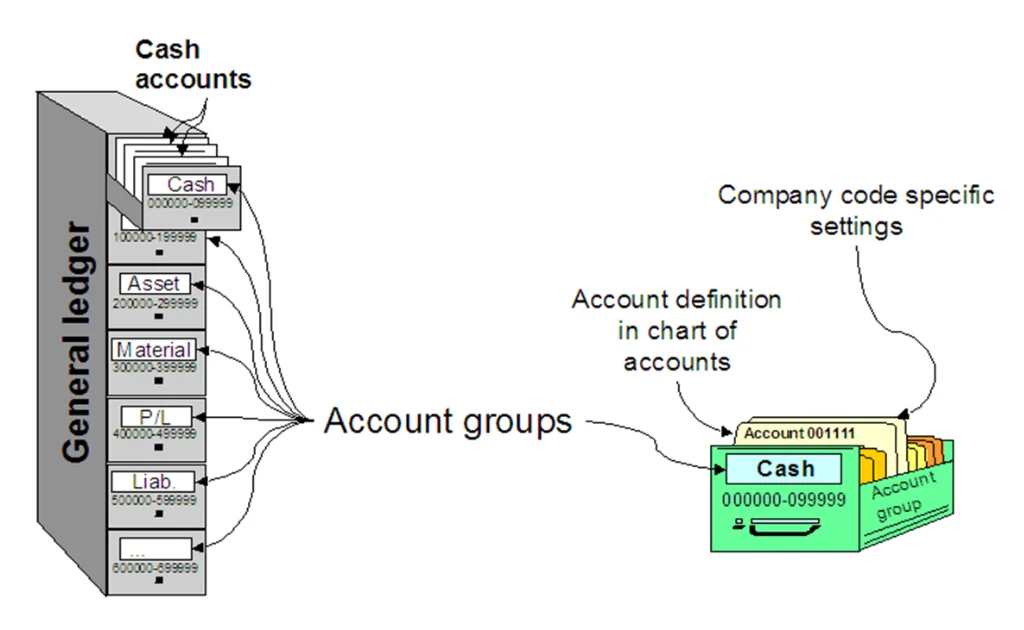
- General Ledger (GL):
- Records all business transactions in real time—income, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
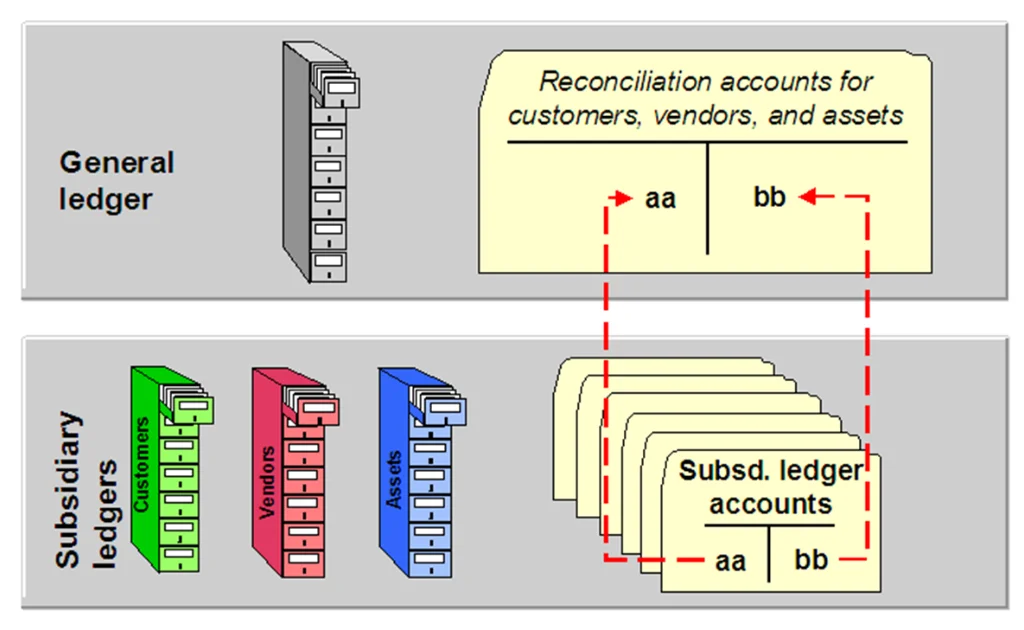
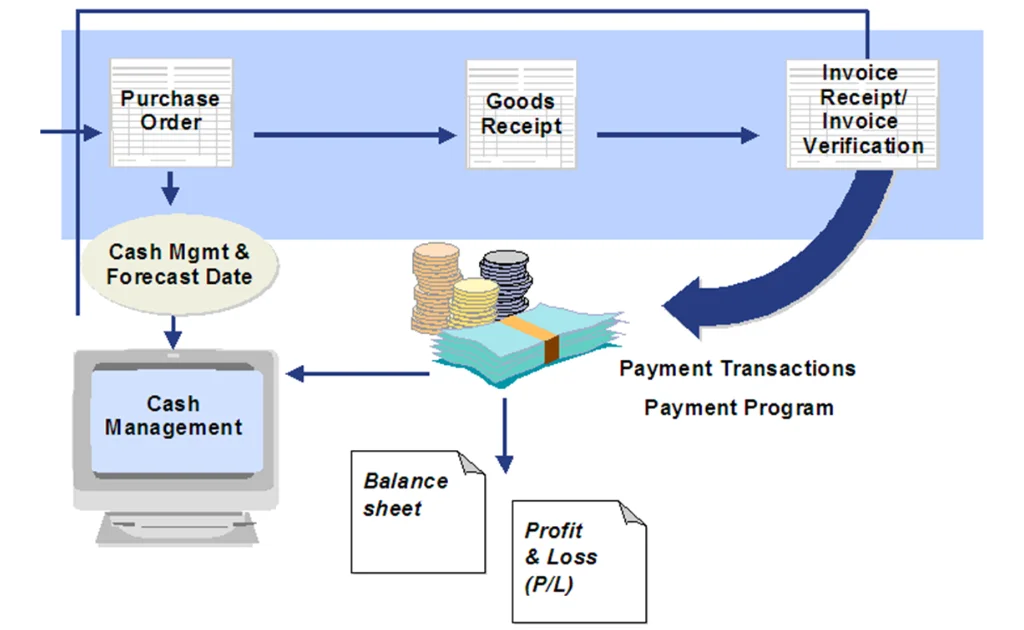
- Accounts Payable (AP):
- Manages vendor invoices, payments, and credits.
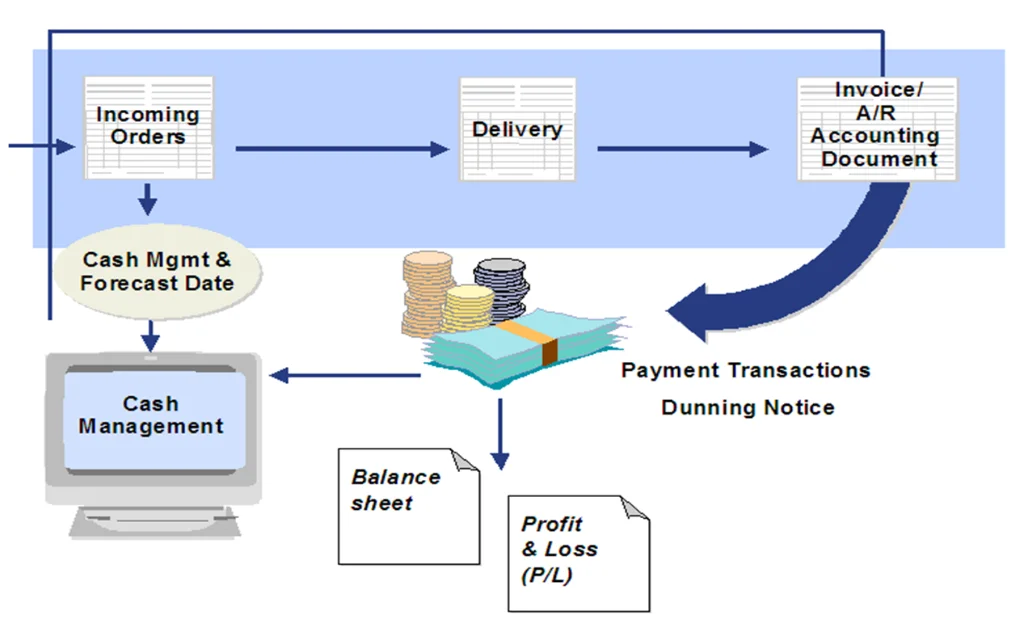
- Accounts Receivable (AR):
- Tracks customer invoices, incoming payments, and credit limits.
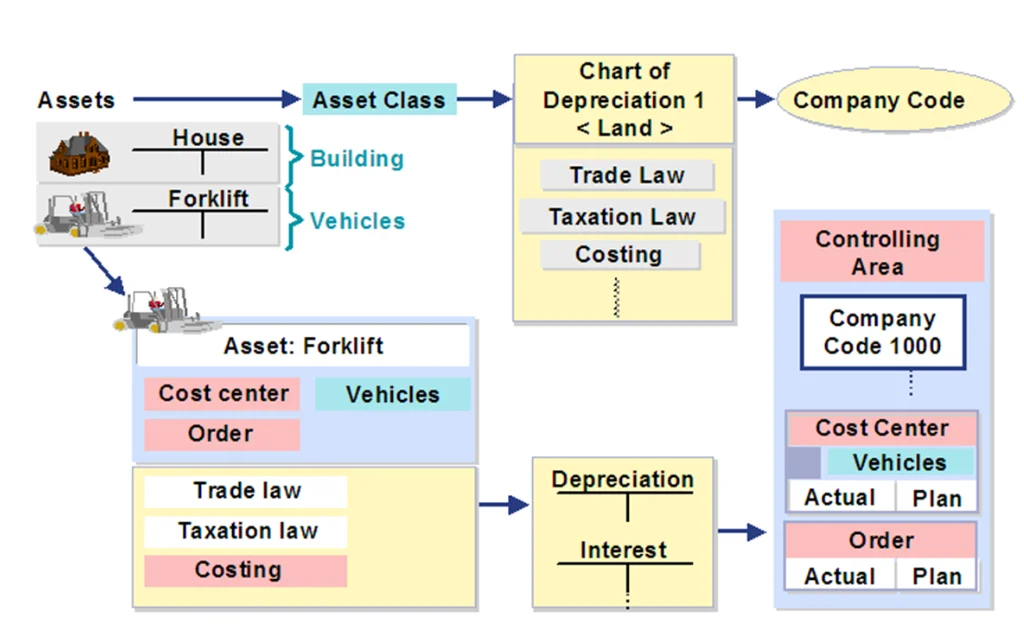
- Asset Accounting (AA):
- Handles the complete lifecycle of fixed assets—from purchase to depreciation and retirement.
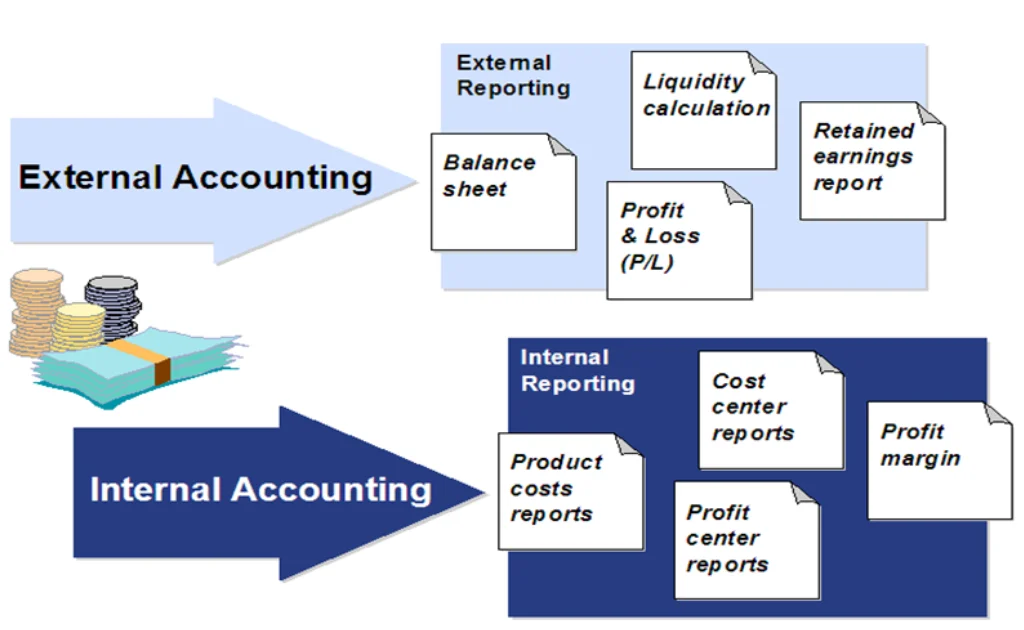
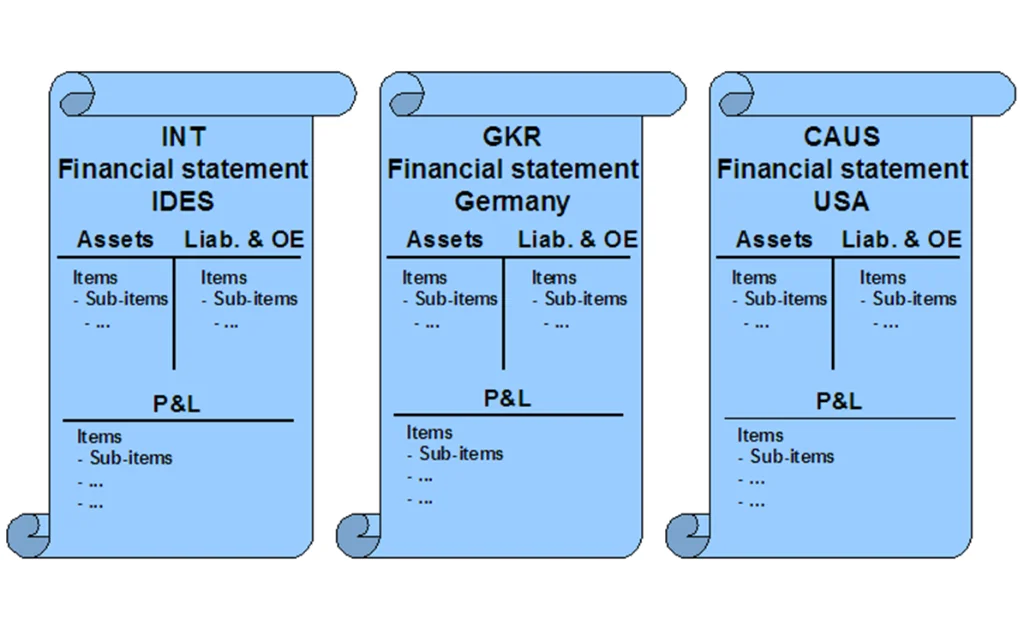
- Financial Reporting:
- Generates legal financial statements like Balance Sheets and Profit & Loss (P&L).
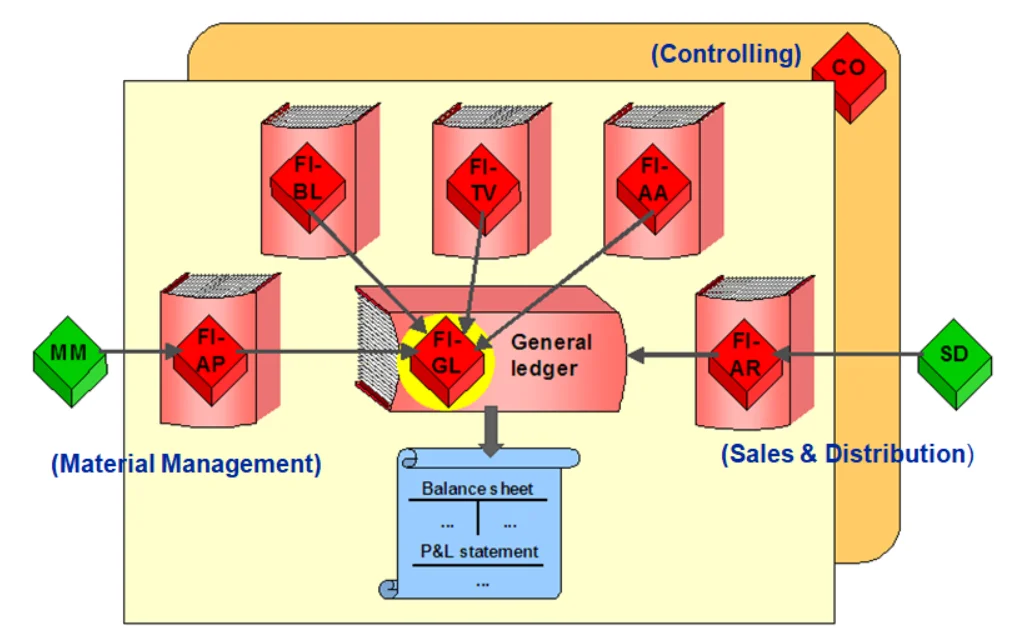
- Integration:
- Seamlessly integrates with other SAP modules like MM (Material Management), SD (Sales & Distribution), and CO (Controlling) for smooth operations and real-time updates.
Why SAP FI is Important:
- Ensures legal compliance and audit readiness
- Provides accurate financial reporting for stakeholders
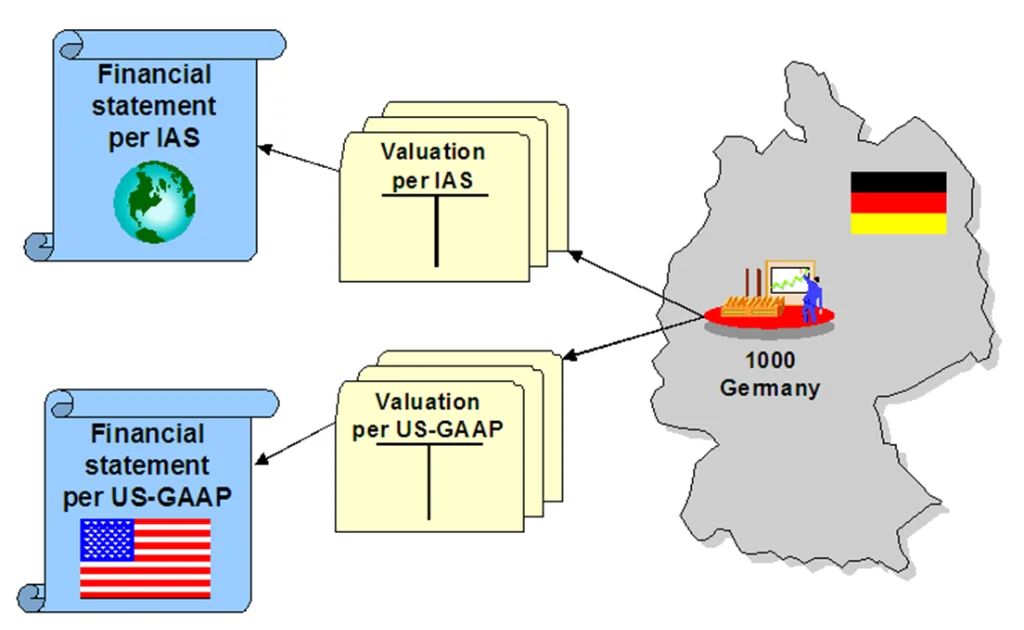
- Enables global operations with support for multiple currencies and country-specific rules
- Helps in decision-making through real-time financial insights
SAP ERP Core Componants