What is SAP MM WM Module – Overview of Material and Warehouse Management
A complete guide to how SAP combines material management and warehouse management for efficient supply chain operations.
Grade a+ Course
Content is Benchmarked by SAP
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
Level 3 – Expert Level Course
Course is designed to prepare you to become a SAP Consultant
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
Overview of Material and Warehouse Management
What is SAP MM WM Module
SAP MM (Materials Management) and SAP WM (Warehouse Management) are critical components of SAP ERP that support the end-to-end procurement, inventory, and warehouse operations of businesses. With deep integration across SAP modules like SD, PP, and FI, MM/WM ensures smooth material flow, vendor coordination, stock visibility, and compliance. This course by Think Tree Technologies is designed to equip learners with real-world skills and SAP configurations that apply across industries.
Key Learning Objectives of SAP MM WM
- Understand the procurement lifecycle in SAP.
- Explore integration with SAP FI and Inventory Management.
- Learn reporting and analytics in procurement.
- Get an overview of configuration using SPRO.
Core SAP MM/WM Topics Covered
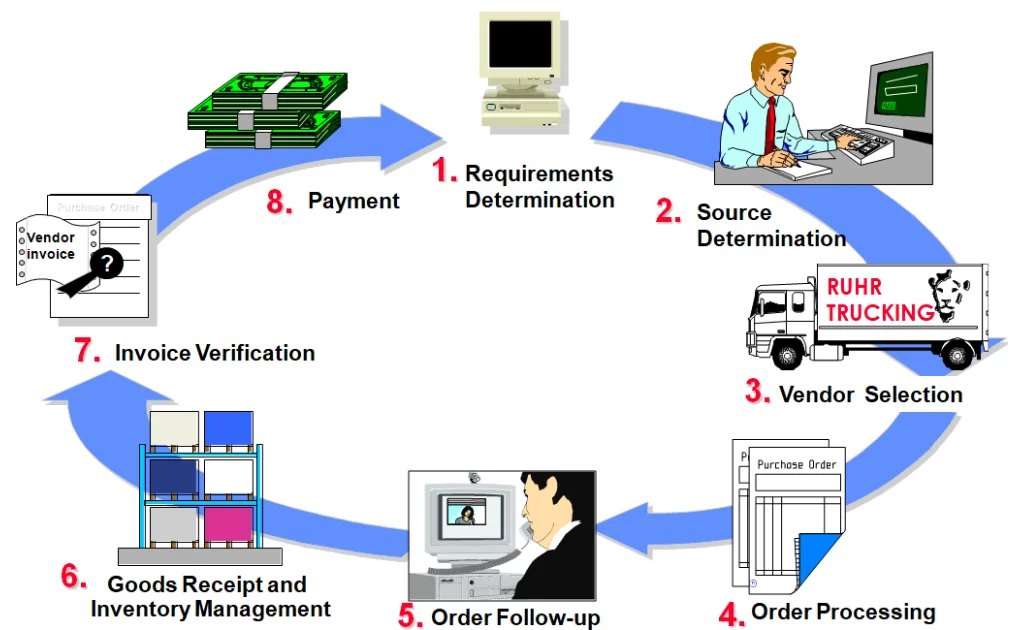
- SAP Procurement Business Process
- Request to Pay lifecycle
- Integration with FI, MRP, and Inventory Management
- Purchase Requisition → Source Determination → PO → GR → Invoice → Payment
- Organizational Elements
- Company Code: Independent legal entity for financial reporting
- Plant: Physical location (manufacturing unit or warehouse)
- Storage Location: Material-level stock control
- Purchasing Org: Controls procurement policies
- Purchasing Group: Responsible buyers or groups
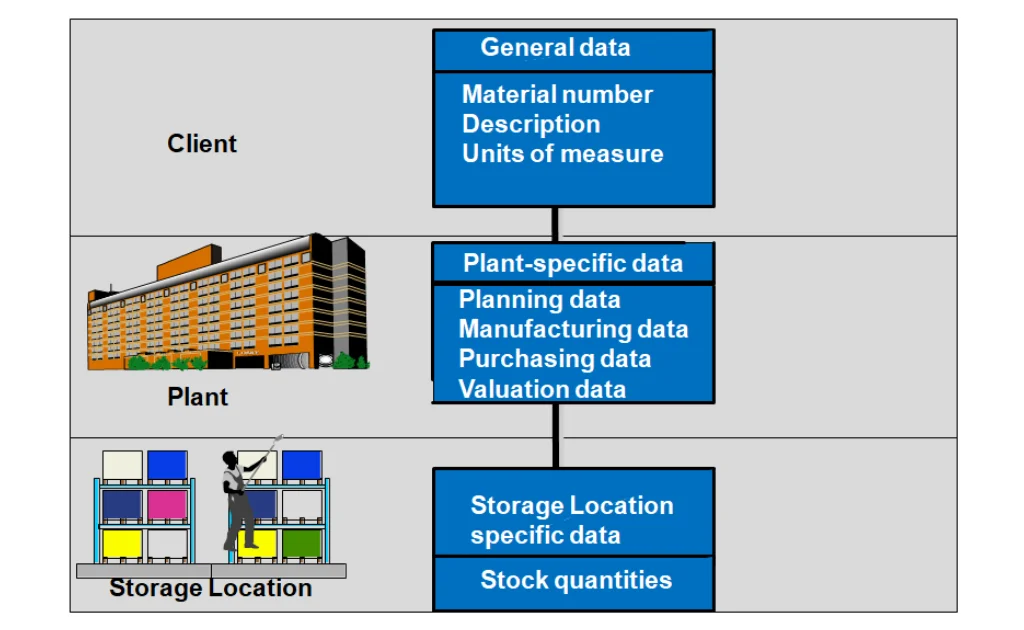
- Master Data in SAP MM
- Material Master: Central database that integrates data across departments
- Key views: Purchasing, Accounting, Storage, MRP
- Vendor Master: Shared between Accounting and Purchasing
- Material Master Organizational Levels
- Client → Plant → Storage Location
- Controls data visibility and configuration options