What is SAP PP Module | Production & Planning | SAP PP Overview
What is SAP PP Module | Production & Planning | SAP PP Overview
Grade a+ Course
Content is Benchmarked by SAP
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
Level 3 – Expert Level Course
Course is designed to prepare you to become a SAP Consultant
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
What is SAP PP Module | Production & Planning | SAP PP Overview
What is SAP Production & Planning
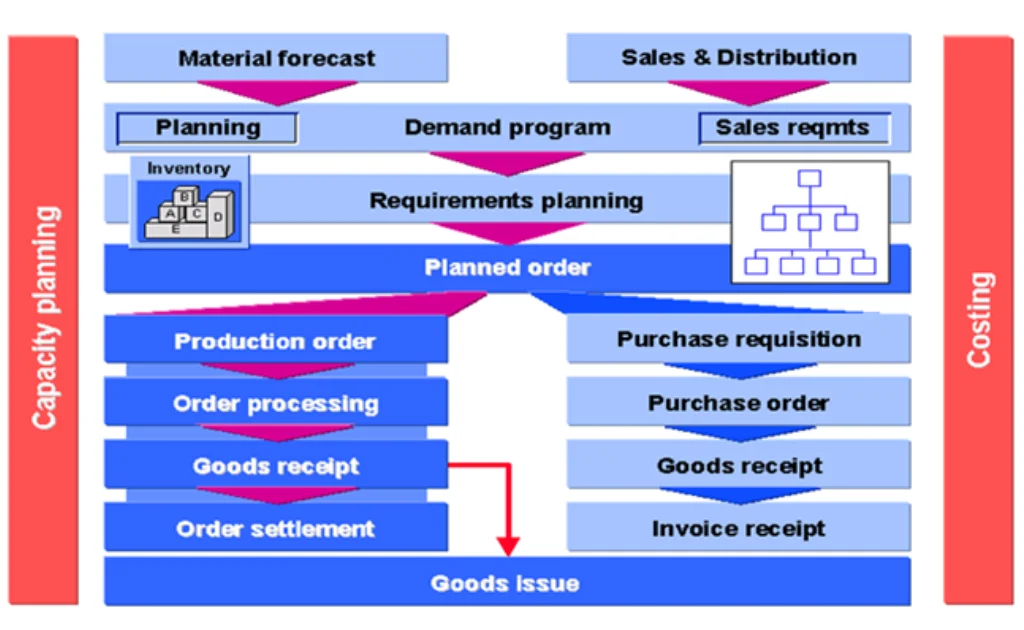
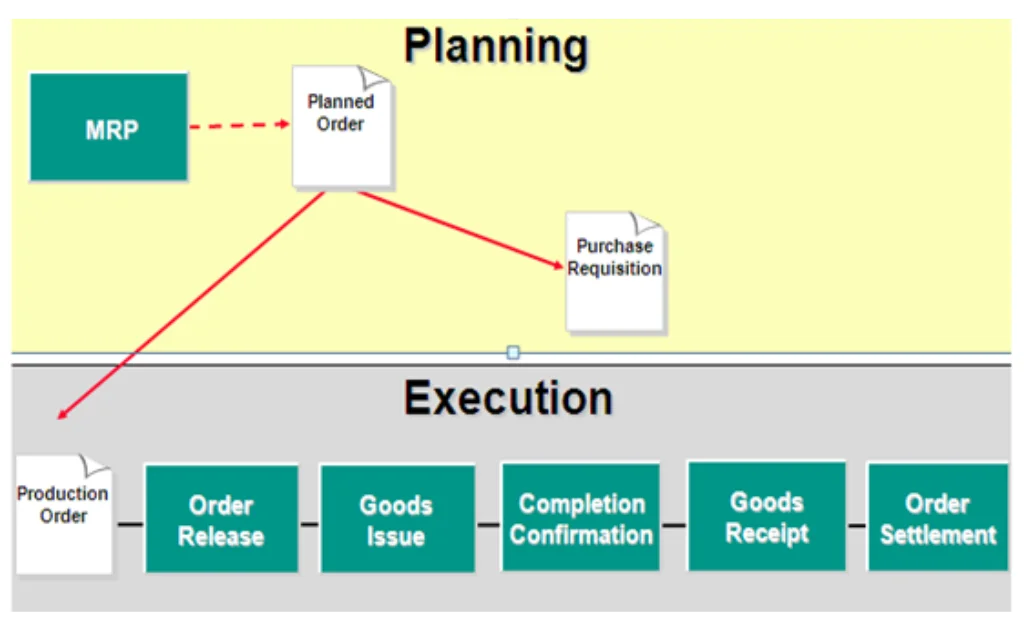
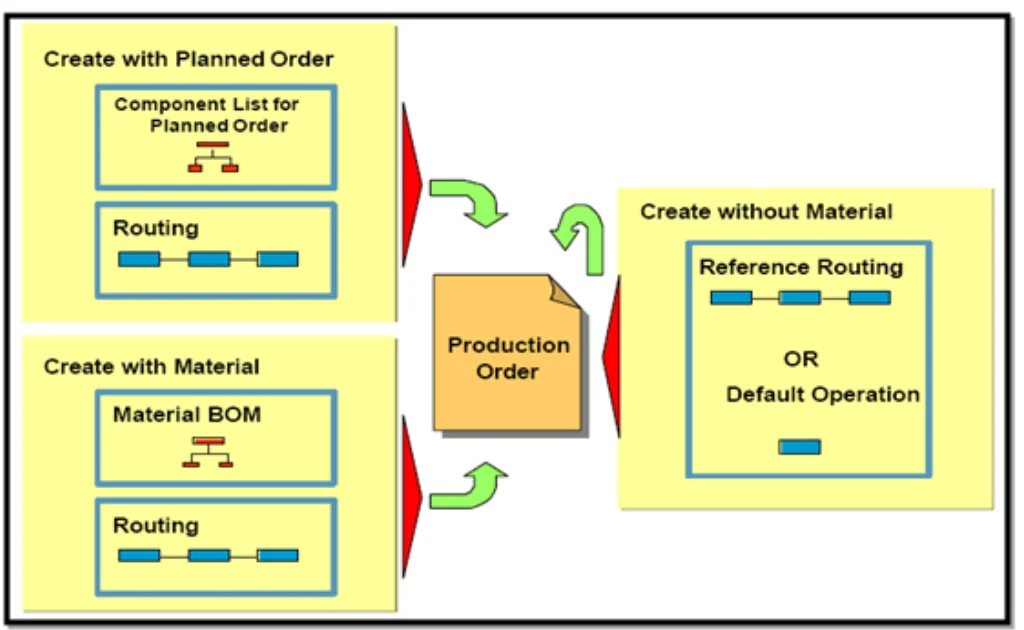
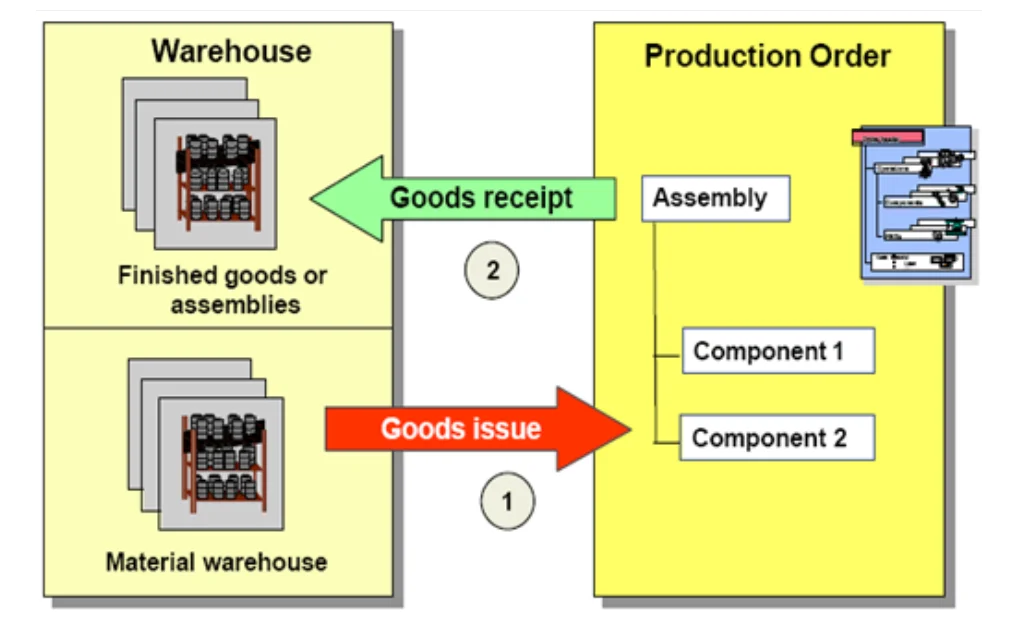
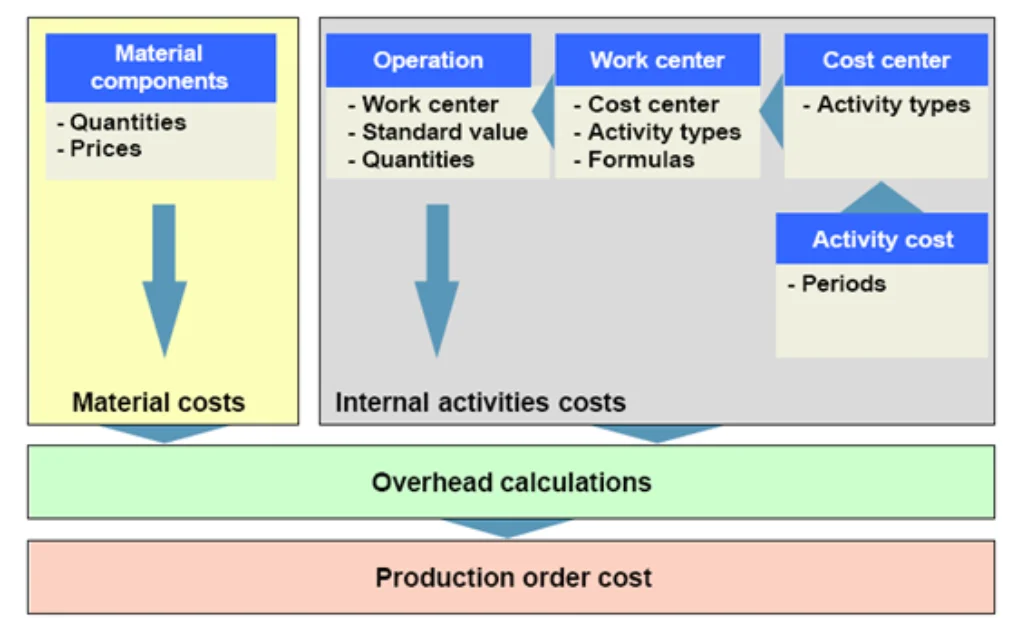
SAP Production Planning (SAP PP) is the heartbeat of manufacturing in the SAP ecosystem. It empowers businesses to efficiently manage the production lifecycle—from demand forecasting and material procurement to order execution and cost control. By integrating with SAP modules like SD, MM, CO, and QM, SAP PP ensures end-to-end visibility, optimized resource utilization, and timely product delivery.
Whether you’re dealing with Make-to-Stock (MTS), Make-to-Order (MTO), or Repetitive Manufacturing, SAP PP delivers a robust framework for planning, scheduling, and controlling all production activities.
Overview of Production Planning (PP)
- SAP PP (Production Planning) is a core module of SAP ERP for manufacturing companies.
- It is tightly integrated with other modules like MM (Materials Management), SD (Sales & Distribution), and CO (Controlling).
- Ensures manufacturing efficiency through planning, execution, and monitoring.