What is SAP SD Module | Sales & Distribution | SAP SD Overview
SAP SD handles end-to-end sales operations, from quotations to invoicing. Learn what the SAP SD module is and why it’s key for business success.
Grade a+ Course
Content is Benchmarked by SAP
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
We are based in New Jersey, USA
26 Wills Way, Piscataway, NJ, USA 08854
Level 3 – Expert Level Course
Course is designed to prepare you to become a SAP Consultant
Trained 10k+ Students
10000+ candidates are trained from our Institute in the last 10 years.
4.8+ rating
Highly satisfied students
What is SAP SD Module | Sales & Distribution | SAP SD Overview
Whats is SAP Sales & Distribution
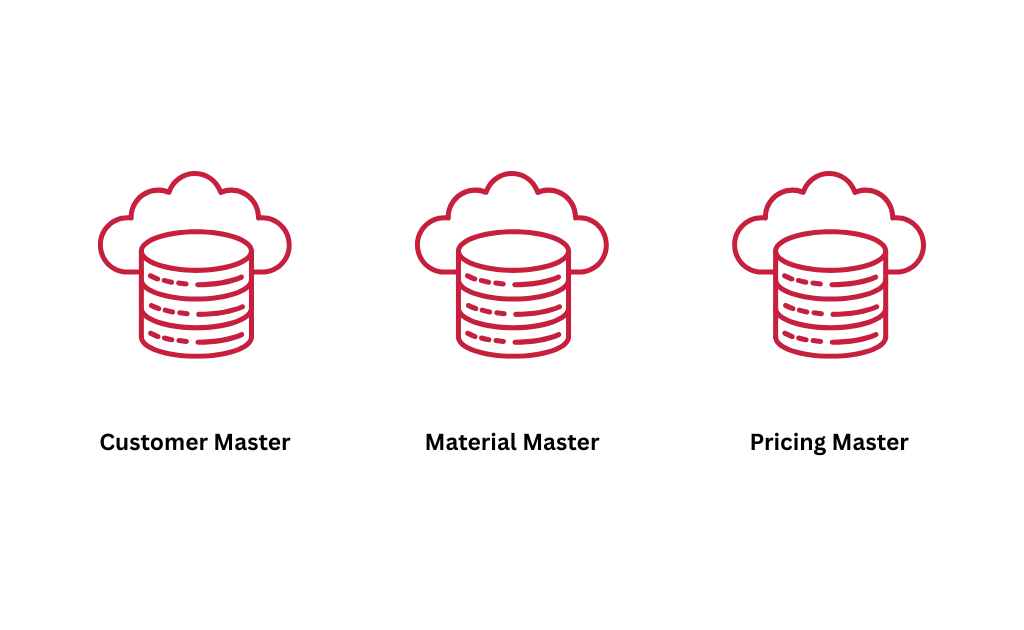
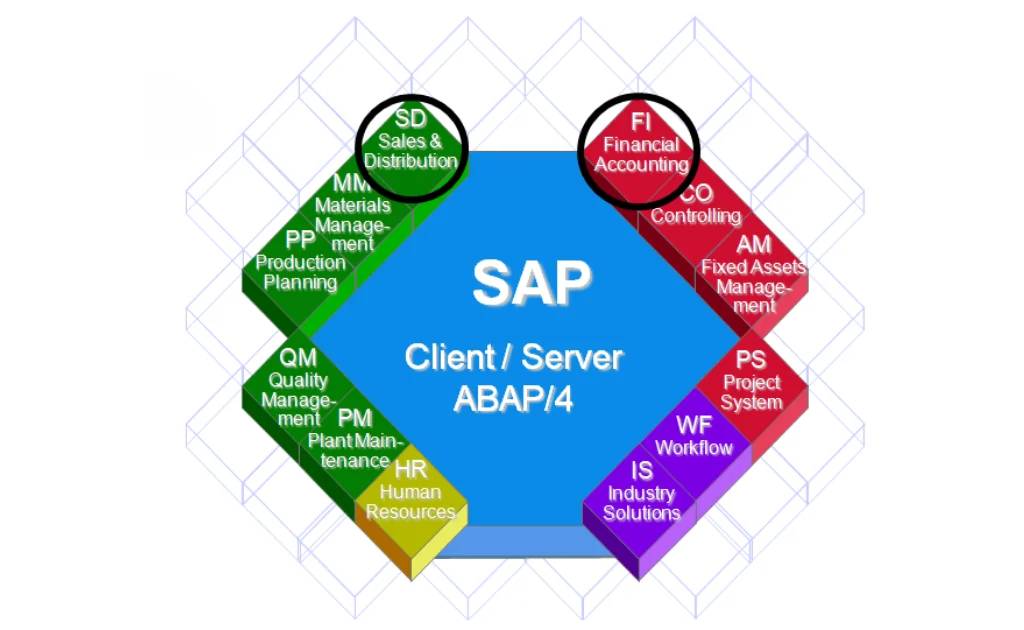
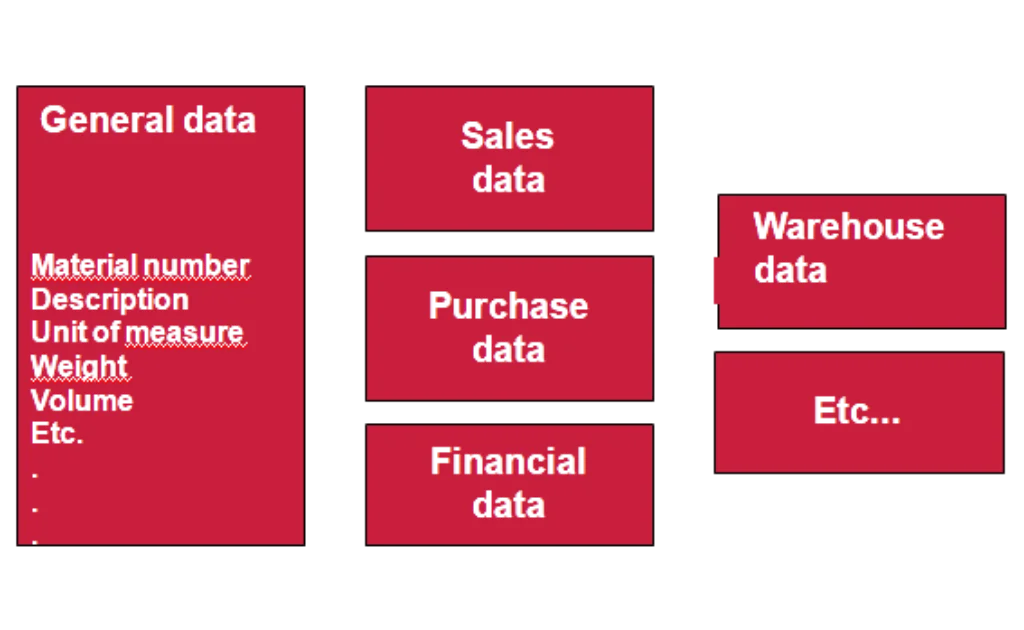
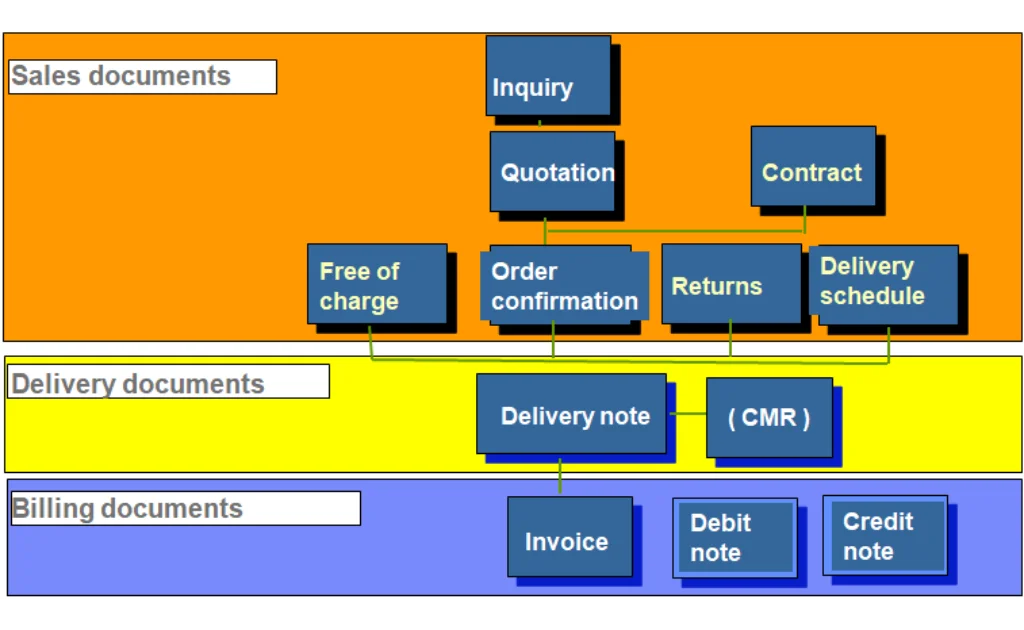
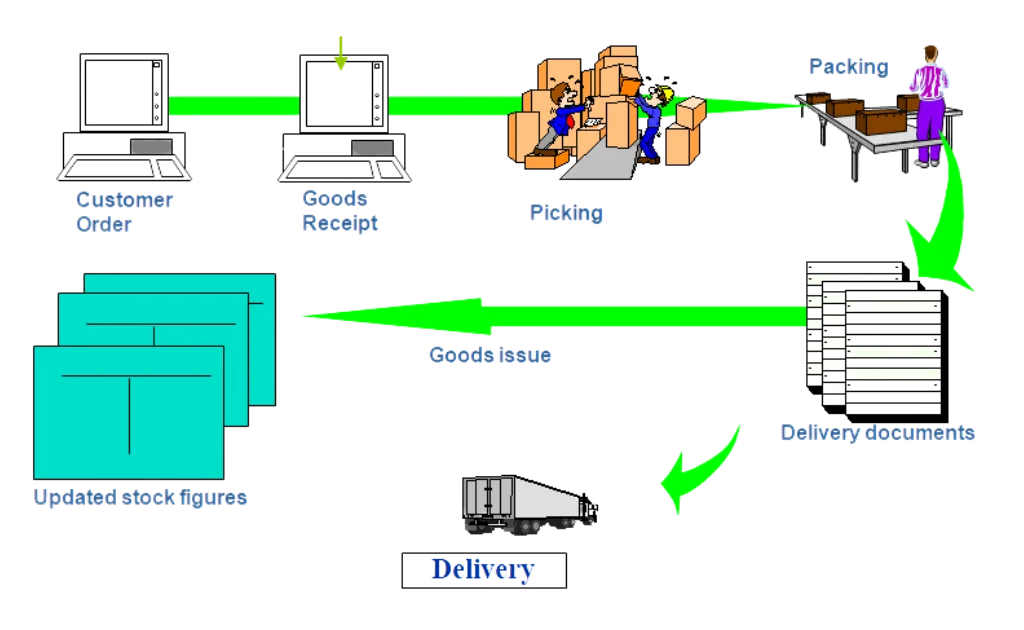
SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) is a core module in SAP ERP that helps businesses manage their entire sales process—from order creation to product delivery and billing. It ensures that customer orders are processed smoothly, stock levels are checked, deliveries are scheduled, invoices are generated, and payments are tracked.
SAP SD – Sales & Distribution
The primary SAP ERP application modules that support the SD process include:
- Sales and Distribution
- Sales
- Delivery
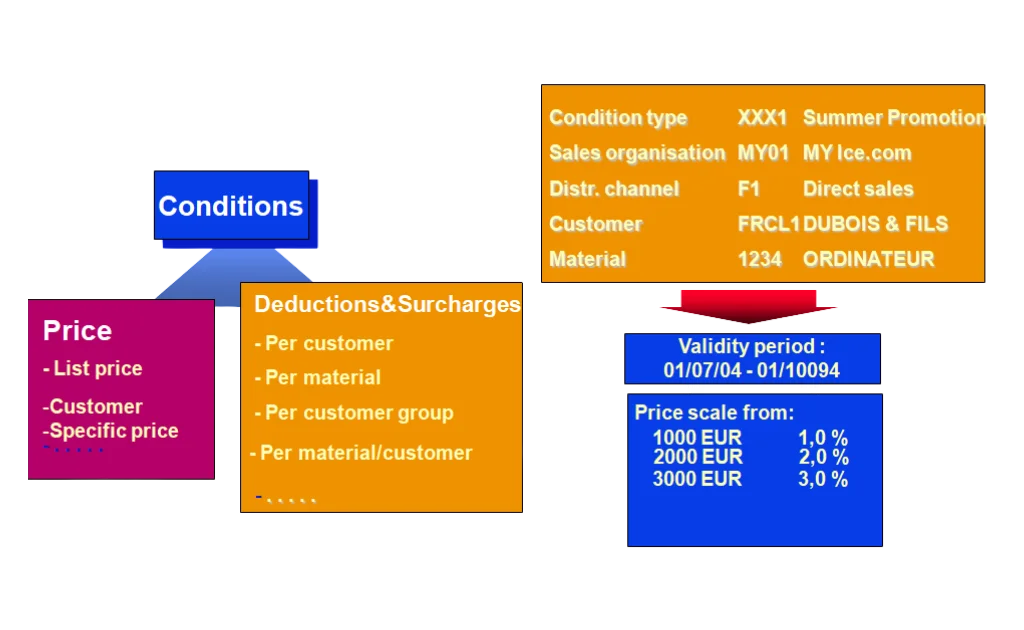
- Pricing
- Customer Billing
- Financial Accounting
- Payment processing
- Materials Valuation